What You Need to Know About an MRI Scan: How It Works, What to Expect, and Why It Matters
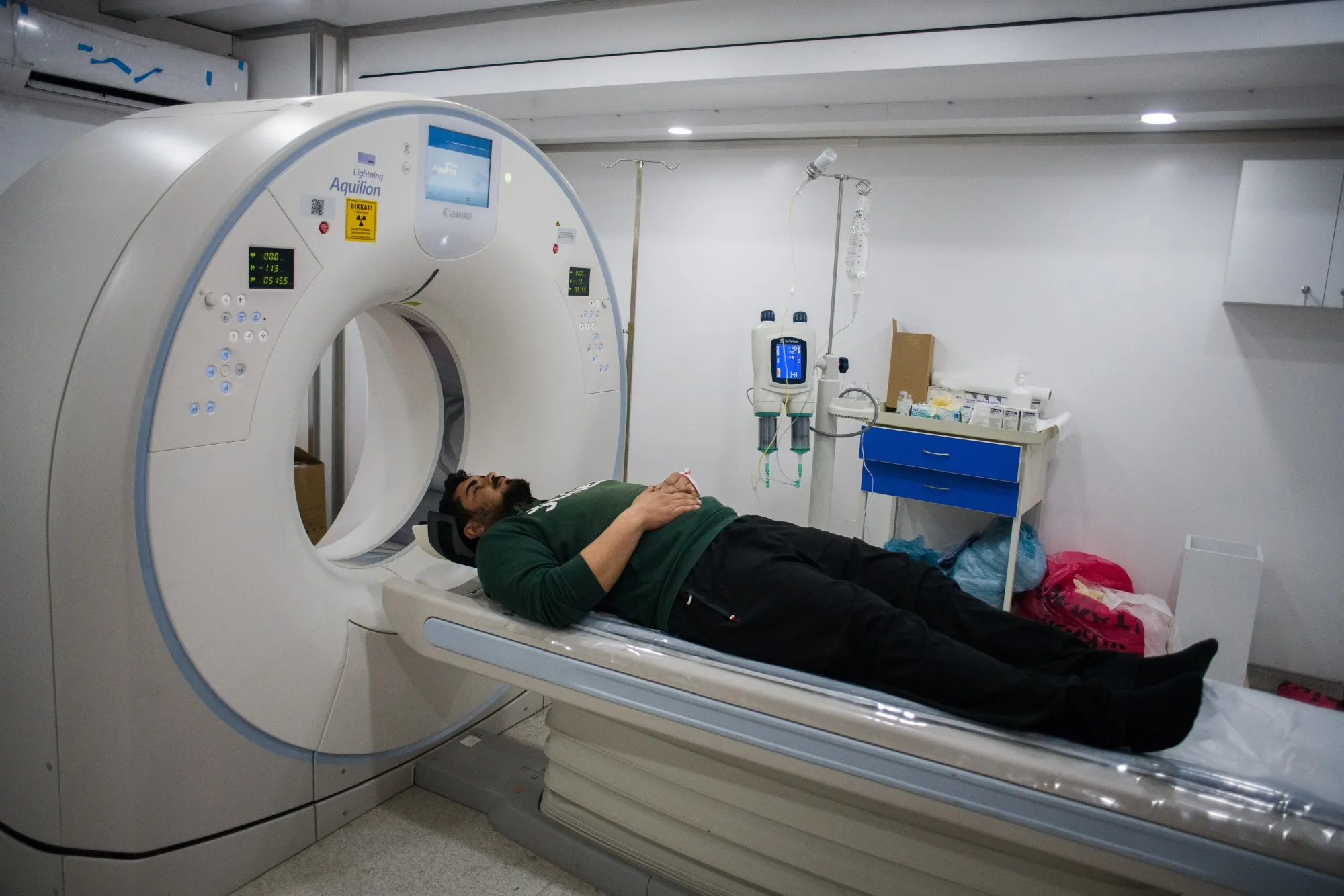
An MRI scan is one of the most powerful diagnostic tools in modern medicine. It can reveal what’s going on inside the human body without a single incision. Whether you’re dealing with a lingering headache, chronic back pain, or an unexplained injury, your doctor might recommend an MRI scan to get a clearer picture—literally.
But what exactly is an MRI scan? How does it work, and what should you expect when you're sent for one? Let’s break it down.
What Is an MRI Scan?
MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. An MRI scan uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of the organs, tissues, and structures inside your body. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, which use ionizing radiation, MRI scans are considered safer because they rely on magnetic energy.
The scan can focus on specific parts of the body—like the brain, spine, joints, abdomen, or blood vessels. It helps doctors diagnose everything from tumors and torn ligaments to strokes and spinal cord injuries.
How Does an MRI Scan Work?
The human body is made up largely of water, which contains hydrogen atoms. When you lie in the MRI machine, the powerful magnets align these hydrogen atoms in your body. Short bursts of radio waves are then sent through, which disturb the alignment. When the waves stop, the atoms return to their original position and emit signals. These signals are picked up by the MRI machine and converted into high-resolution images.
The result? A detailed cross-section of the body part being scanned—layer by layer.
Why You Might Need an MRI Scan
Doctors don’t order MRI scans without a reason. They're typically used when other imaging tools don’t provide enough information. Some common reasons for an MRI scan include:
-
Brain and spinal cord issues: To detect tumors, multiple sclerosis, strokes, or brain injuries.
-
Joint problems: To assess cartilage damage, ligament tears, or inflammation.
-
Heart and blood vessels: To examine heart structures or check for blocked arteries.
-
Internal organs: To evaluate kidneys, liver, pancreas, or reproductive organs.
-
Cancer diagnosis: To locate tumors, assess their size, or monitor treatment progress.
An MRI scan gives doctors a non-invasive, 3D look inside your body, helping them make more accurate diagnoses.
What Happens During an MRI Scan?
The MRI process is simple, but it can feel intense for some people.
-
Preparation: You’ll be asked to remove all metal items—watches, jewelry, belts—because metal can interfere with the magnets. You’ll change into a hospital gown to ensure safety and comfort.
-
Positioning: You’ll lie down on a flat table that slides into a large, cylindrical MRI machine. The technician might give you earplugs or headphones to help block out the loud banging noises the machine makes.
-
Staying Still: You must lie very still during the scan. Even small movements can blur the images. Scans usually take between 15 and 60 minutes, depending on what part of the body is being scanned.
-
Contrast Dye (Optional): In some cases, a contrast agent like gadolinium is injected into your vein. This helps enhance certain tissues or blood vessels in the images.
-
Completion: Once the scan is done, you’re free to go unless you’ve been given a sedative. There’s no recovery time, and most people return to normal activities immediately.
Is an MRI Scan Safe?
For most people, yes. MRI scans are painless and non-invasive. They don’t involve harmful radiation, making them safer than some alternatives.
However, they aren’t suitable for everyone. People with pacemakers, cochlear implants, or certain types of metal implants may not be able to have an MRI scan due to the magnetic field. Always inform your doctor or technician about any implants, metal fragments, or medical conditions.
MRI vs. Other Imaging Methods
MRI scans stand out for their clarity and detail, especially for soft tissue imaging. Here’s a quick comparison:
-
MRI vs. X-ray: X-rays are better for bones. MRI scans are better for soft tissue.
-
MRI vs. CT scan: CT scans are faster and better in emergencies (like detecting bleeding). MRIs take longer but show more detail.
-
MRI vs. Ultrasound: Ultrasounds are cheaper and faster, but MRIs provide much higher resolution.
Each has its place. But when doctors need precision and detail, an MRI scan is often the go-to.
The Bottom Line
An MRI scan isn’t something to fear. It’s a high-tech, non-invasive way to see deep inside your body. It plays a crucial role in diagnosing conditions early, tracking disease progression, and guiding treatment decisions.
If your doctor recommends an MRI scan, take it seriously—but don’t stress. It’s one of the most advanced and reliable tools in healthcare today. And when it comes to your health, clear answers matter.
- Art
- Causes
- Best Offers
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jeux
- Festival
- Gardening
- Health
- Domicile
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Autre
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



